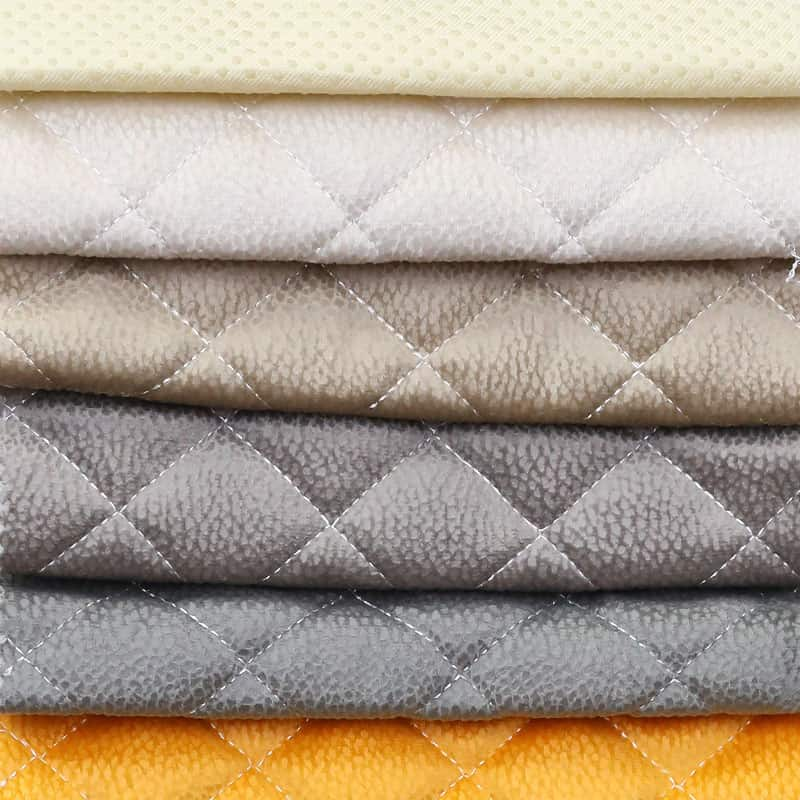
The classification of textile fabrics is the basic unde […]
The classification of textile fabrics is the basic understanding of fabrics. To learn the classification of fabrics, to understand the weave and structure of fabrics and the raw materials of fabrics is the most important point for entering the textile industry. For the raw materials of fabrics, there are also fabrics. Knowing the style and characteristics is of great help to us. Here is a summary of modern fabrics based on the classification of raw materials.
Classification of fabrics
(1). Fabrics are mainly divided into: non-woven fabrics and textile fabrics. According to the raw materials of textile fabrics, they can be divided into natural fabrics and non-natural fabrics.
1. Natural raw materials can be divided into:
1.1. Plant fiber, such as cotton, hemp, fruit fiber
1.2. Animal fibers, such as wool, wool-free, silk
1.3. Mineral fibers, such as asbestos
2. Non-natural raw materials are divided into:
2.1. Regenerated fibers, such as: viscose, acetate, tencel, modal, lyocell, bamboo fiber, etc.
2.2. Synthetic fibers, such as nylon, polyester, acrylic, spandex, Lycra, etc.
2.3. Inorganic fiber, such as: glass fiber, metal fiber, etc.
(2) From the perspective of textile technology:
Woven: The woven fabric has a stable structure, no elasticity (except for the fabric with elastic fiber), the cloth surface is flat, solid and durable, the appearance is crisp, loose, simply speaking, it is not close to the body, and it will not be visible if it is broken and scratched.
Knitting: Knitted fabric is full of elasticity, the cloth surface feels soft, comfortable and fit, breathable, easy to loose. To put it simply, the bigger the crossing. It was broken and pulled a hole.
Grade of fabric
The grade level of the above raw materials can be divided into the following levels: (do not distinguish between printing and dyeing processes)
Low-grade fabrics: ordinary chemical fiber, like polyester filament or staple fiber, nylon filament, rayon, etc.
Ordinary fabrics: general cotton, nylon hollow yarn and stretch yarn.
Intermediate fabrics: linen, Lycra, Tencel and other intermediate chemical fiber fabrics and natural and blended fabrics, tussah silk, long-staple cotton, ordinary leather, etc.
High-grade fabrics: wool, mulberry silk, (fabric), calfskin, lambskin and other leather materials, fox skin and other ordinary fur
Top fabrics: sheep (camel hair), heavy mulberry silk fabric, precious leather, mink and other high-end furs.
Advantages and disadvantages of various raw materials
Ordinary chemical fiber fabric: good strength, good corrosion resistance, but poor moisture absorption and breathability, uncomfortable to wear.
Cotton fabric: Below ordinary long-staple cotton, it will become hard after washing many times
Color cotton fabric: only two colors of brown and green
Linen fabric: not wrinkle-resistant, easy to fade, easy to shrink mold
Ordinary silk fabrics: easy to shrink, intolerant to acids, and resistant to sunlight
Wool fleece fabric: easy to grow insects. To
Artificial cotton fabric: easy to stick to the body
Modal fabric: easy to pilling and wrinkles
Tencel fabric: the hot and humid environment hardens
Ice silk fabric: easy to lose silk and harden
Bamboo fiber fabric: perishable
